A Scheme for Robust Distributed Sensor Fusion Based on Average Consensus
Highlights
-
Voted test of time paper at SenSys. Provides a great diving board for current works involving distributed consensus algorithms.
-
Despite the density of this paper, the core spirit of the algorithm is relatively easy to implement and can be easily extended upon.
Summary
The authors present a simple distributed iterative scheme that computes the maximum-likelihood estimate of parameters using distributed average consensus. The algorithm does not depend on explicit point-to-point messaging or routing, instead, it communicates purely with it's neighbors. Collectively, this allows the network to converge to a global maximum-likelihood solution and provides intermediate estimates that are practically valuable. The authors show that their scheme is robust changing topology with link failures and unreliable communication links.
Key Contributions
- A simple distribtued iterative scheme that computes the global maximum-likelihood solution against any dynamically changing network topology (given the condition of at least joint-connectivity), and is robust to link failure and unreliable communication links
Strengths
-
The paper is rigorous in it's demonstrations that the algorithm converges, even along link failure and unreliable communication links
-
The authors make a point to state the conditions in which their algorithm works, and when it doesn't
Weaknesses / Questions
-
The paper is fairly dense and heavy; it's easy to lose one's way when reading it. I feel like sections such as the proofs could be moved to an appendix section at the back.
-
If using in a complex environment, like monitoring the temperature at certain points in a complex differential system, this system will likely do terribly. I feel there are stronger algorithms out there for actually using this in the realistic environmental monitoring setting.
Related Work
-
Distributed Sensing
-
Distributed Consensus
Appendix (Algorithm example)
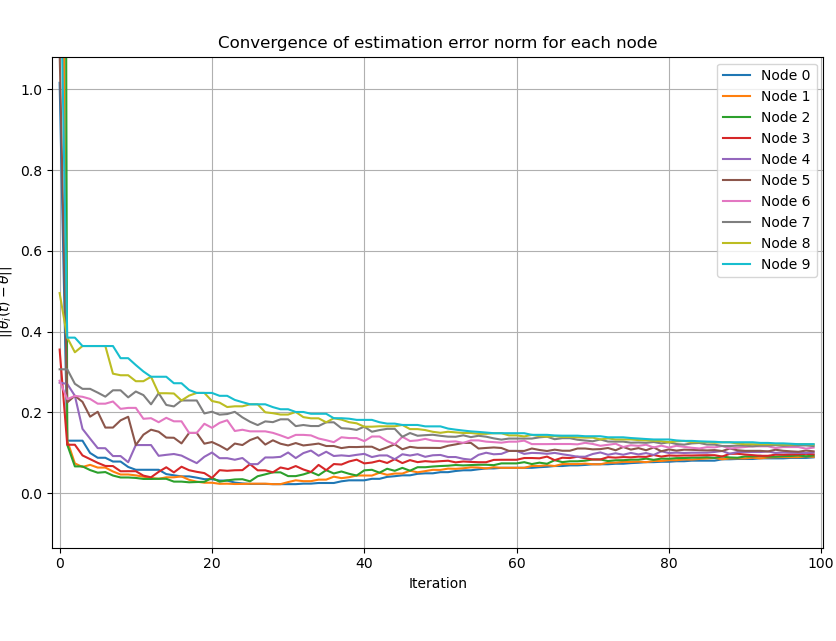
Here's a quick implementation of their algorithm written in Python, showing it converging along a randomly connected topology of 10 nodes. The increasing infima and decreasing suprema over time is really cool to see.